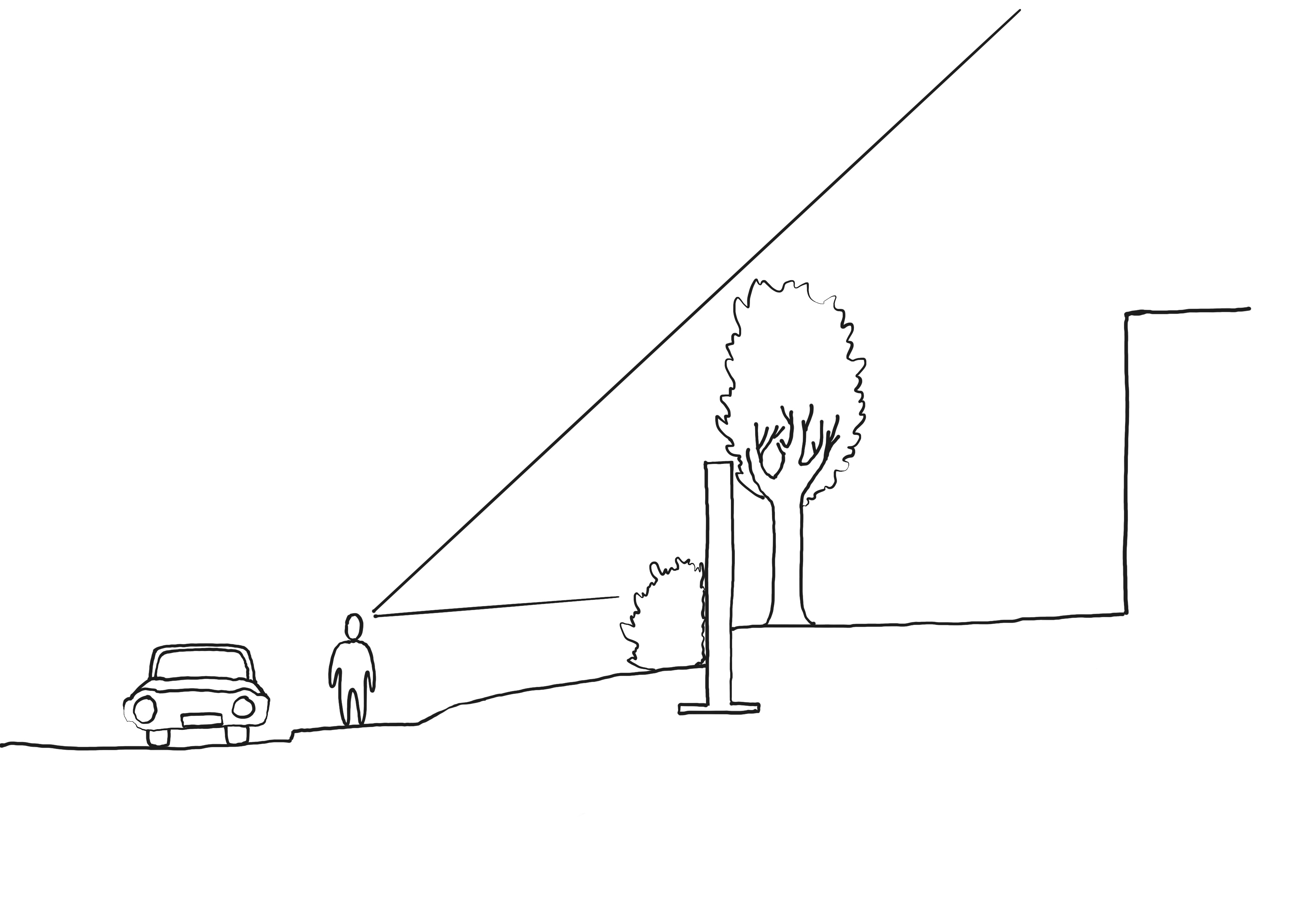
Protection against surveillance
Terrorists can use sensitive information obtained through surveillance – also known as reconnaissance – in planning an attack against an organisation. If an organisation wants to protect itself against surveillance, a risk assessment should be performed to ensure that the security measures match the actual need.
A potential attacker can use various methods to monitor their target. This includes physical surveillance, where a person physically follows and collects information about their target through e.g. observation, human sources or online sources.
Electronic surveillance can involve bugging, scanning and recording. When installing Technical Surveillance Counter Measures (TSCM), it is therefore important to take a holistic approach to, e.g. a specific room to be secured. This includes attention to the room's location in the building, fixtures, electronic equipment, supply ducts and physical security. TSCM thus covers specific technical protection activities such as the detection of bugging equipment or hidden cameras.
Common to both surveillance methods is that they can be counteracted by counter-observation, as well as different technical solutions that can be part of the organisation's security set up and security culture. To achieve holistic protective security, one must therefore generally abide by the same principles that apply to information security. It should be noted that, in addition to the examples described above, surveillance may be carried out by a combination of methods and methods not yet known.